We know the car can’t function without that motor but we still haven’t really gotten our head around that whole ‘electric car’ thing if we’re honest with ourselves.
In my last article, I tried to make Bitcoin a bit more palatable, but I don’t think it would be complete without at least touching a bit more on the heart of the technology that runs Bitcoin. The reality is it might shape everything from the way our election votes are tallied, to legal contracts, to how titles are transferred when you buy your next home.
To attenuate boredom and at the risk of retraumatizing myself from my many failed elementary school attempts at what few would loosely call ‘art’, I decided to (try to) draw and explain this.
So imagine you and 4 strangers all go into a house and each of you go into separate rooms. The five rooms combined form the shape of a circle. In the middle of this circle is another room. We’ll call this the transaction room. You cannot enter this room. Your room as well as the other four have a small mail slot that allows you to send and receive money through to a person on the other side who’s sitting in this transaction room. Let’s call this person Bank.
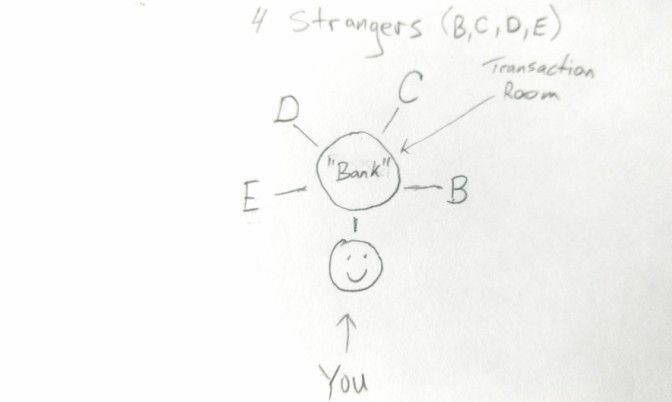
Now let’s say you want to send $100 to ‘stranger B’. Your normal process (how we currently do things in the world) would be to slide a $100 through the mail slot, into the transaction room with a note to tell Bank to give your $100 to ‘stranger B’. Bank would then pass along your $100 to stranger B (sometimes taking let’s say $2 as a fee for her hard work of transferring that money for you) and would record this transaction on behalf of both of you.
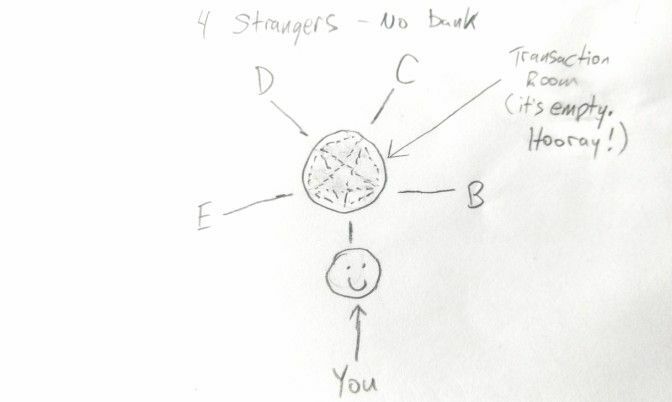
With Blockchain Technology, Bank is no longer around and essentially the transaction room is empty. Instead, when you want to send money to ‘stranger B’, this time you have the ability to reach through and put the money directly into the mail slot of ‘stranger B’.
This transaction is called a ‘block’. To avoid fraud, a random encryption number (called a “hash”) is created. Let’s make one up for this transaction and say your “hash” is 123syu.
After this encryption number has been created, this “block” is now added to the chain of other transactions (“blocks”) within your group of strangers, hence the name “block”….”chain”.
See chain links in my fine art below.
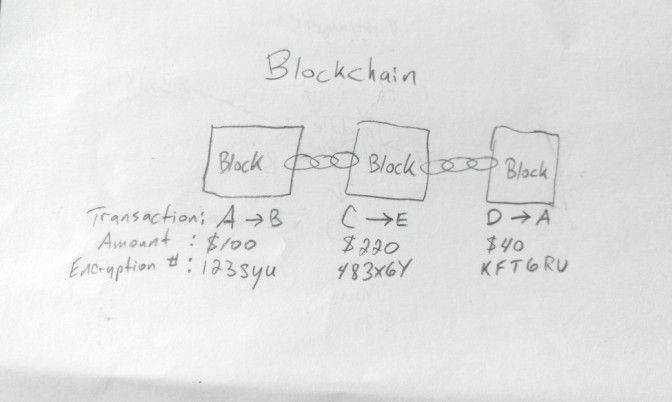
Everyone (including you) in the circle keeps a record (called a ledger) of each transaction on the entire blockchain, ensuring that no single individual or group can tamper with the chain or try to change the figures. If an attempt were made, others would notice that their ledger does not align and therefore would reject it.
That’s it. Clear as mud right?
I’ve simplified a couple things but, this is the general foundation of Blockchain and it’s the technology that’s the engine of cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin. Almost all of what was explained above are done by thousands of computers around the world in fractions of seconds, which is one of the major selling points of the technology in addition to how it can help alleviate fraud by keeping thousands of strangers honest.
You may not believe in, like or trust Bitcoin for a variety of reasons, but Blockchain Technology, while there still is some unjustified hype, might be the real deal for years to come.
David Green is a Full-Stack Web Developer and a serial entrepreneur. He has business and sales background for Fortune 500 companies and his own startups and has a deep passion for social and economic equity. His most recent endeavour is founding & leading Devslove, a web development digital growth agency.








